Menu engineering: Popularity and contribution to gross margin
Le menu engineering est définit comme un excellent outil de choix de plat de définition de prix dans un restaurant. Les experts l’utilisent pour améliorer la gestion et les bénéfices des restaurants.
Mais qu’est ce que le menu engineering ?
Le menu engineering, traduction “Ingénierie des menus” ou comment augmenter les bénéfices de son restaurant de 15% ou plus. Tout d’abord, le menu engineering est l’étude de la rentabilité et de la popularité des éléments du menu. C’est la façon dont ces deux facteurs influent sur le placement des plats sur un menu. Enfin, l’objectif est donc très simple : augmenter la profitabilité par client.
Quel est l’objectif du menu engineering ?
Tout d’abord, l’objectif du menu engineering “ingénierie du menu” en restauration est donc de maximiser la rentabilité d’un restaurant en incitant inconsciemment les clients à acheter un certain plat. Ces plats seront donc ceux qui rapportent le plus.
Par ailleurs, les champs d’exploration qui contribuent ces études comprennent:
- Psychology: customer perception and attention
- Analysis of the contribution to the gross margin of items and their unit cost (food cost)
- Marketing and pricing strategy
- Card Design and Graphic Design and Sales Support
Free Trial | Koust Application
- Learn how to design your restaurant's menu to get more profit.
- Get 15% continuous improvements from the time you redesign your menu.
- These strategies apply to all types of ranges: traditional menu, wine list, dessert, drinks and more.
Analysis of your card by the Engineering Menu
Comment mesurer la contribution des plats à la marge brute du restaurant, par la méthode appelée “Menu Engineering”. Par cet outil, on classe les produits (plats, boissons) dans un tableaux ou matrice à 4 cases en fonction de la marge brute sur un axe et en fonction de la réputation du plat sur l’autre axe. Enfin, cette technique permet donc de visualiser un plat très considéré et très rentable d’un seul coup d’oeil.
Thus, dishes are classified into ranges to compare them more effectively:
The contribution to the margin in a restaurant
Dans une gamme, un plat est classé en fonction de sa marge unitaire en valeur. Donc plus le profit est élevé plus sa participation à la marge globale du restaurant est forte et inversement. Le prix unitaire du plat n’est pas prioritaire.
The popularity of your dishes
Within a range, a dish is ranked according to its sales relative to other dishes in that range.
Popularity Chart / Margin
We divide into 4 cases corresponding to the two criteria reputation and gross margin of a dish.
| low ratio |
strong ratio |
|
|
Strong Popularity |
Plow horse Popular low ratio product or dish. they often constitute the reputation of the business |
Stars
Popular and profitable dish. |
| Low Popularity | Dead weight
dishes or products neither popular nor profitable. |
Puzzles The products and puzzle dishes are not highly regarded but their margin is good. |
Highlighting of dishes according to their classification
Star products :
They must be "highly visible" on the map and recommended by the sales staff.
Products Work horse (or cash cow) :
Don't spend energy putting them on first, they sell themselves.
The Product Riddle (or dilemma):
Check their visibility on the map or change their name.
Products Dead weight :
Try to remove them or at least not promote them.
Limitations of using the engineering menu calculation
This calculation is a statistical method and therefore requires a minimum of sources. Moreover, it is difficult to use it for the dishes of a menu or for the menus? Finally, it is possible to compare each menu with each other, but it is more difficult to compare their composition dish by dish. The menu will have its own selling price but it is composed of several dishes, so the ratio is calculated at the level of the menu and not of the dish.
For products that are not on the menu all the time, such as daily specials, the presentation must be included in the calculation. That is to say the number of times the dish has been proposed in the month for example.
In this case, the number of sales of the dish is divided by the presentation percentage of the dish. Percentage of presentation of the product = number of presentations of the product / number of presentations of all products in the range)
Method of calculating the engineering menu
What data and how to calculate?
- The first step is to group the products on sale by range (category): starters, main courses, desserts, red wines, soft ...
- Then, in each range, we will group together the figures and compare the different products on sale: quantity sold, selling price excluding VAT, unit material cost or purchase cost of the product. (see example below)
The material cost is the total of the recipe's technical sheet or, more simply, the cost of the dish in food ingredients. - The third step is to calculate the values needed for ranking in the BCG matrix (Popularity/Margin Matrix above).
We need two clues:- popularity: the number of sales.
- contribution to the margin: what the dish brings in. This is the selling price of the article - the cost of the article.
- The fourth step is to construct the table and to do this we need the medians (middle rows). Here we take the average sales and the average cost/price ratio, the profit.
Average sales = total sales / number of dishes
Average margin = total gross margins / number of sales (food profit margin) - Finally, the various items in this table are classified according to their number of sales and their contribution to the margin. They are then placed in one of the 4 boxes.
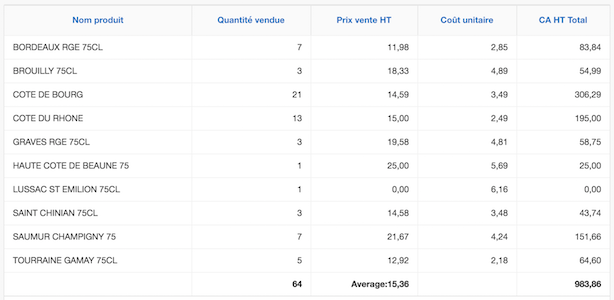
Example of the analysis of a restaurant menu
This table allows you to analyse each red wine sale and price by the menu engineering method, for example.
What do we do with these results?
Une fois cette matrice construite, le travail d’analyse commence. Le chiffre d’affaire et surtout les gains vont croitre en augmentant le choix des articles les plus rentables et les plus populaires auprès de vos clients. En utilisant le neuromarketing on peut revoir la disposition des plats sur la carte, peut-être revoir certains prix unitaires ou renommer certains plats peu attirants.
STAR dish: duplicate these products or dishes in similar products. They should be promoted. These dishes are very profitable and your customers love them.
Dilemma dish: Check the visibility of these dishes on the menu. If necessary, change the name of the product to something more attractive. The price of the dish can also be reduced.
Plough horse dish: These products or dishes sell themselves. They bring in less money, so no unnecessary expenses. The customers of your restaurant like them, these dishes are essential to your reputation. If the price of the dish is well priced, an increase in the price of these dishes could lead to a drop in sales.
Dead weight dishes: If it is not compulsory for certain constraints to keep them, remove these dishes from your menu! If some customers still order them, they are on average in the minority.

In Koust, the data is represented graphically with the number of sales on the x-axis and the gross margin on the y-axis. In Koust we have added the price to complete the information, the unit price is represented by the size of the circle, the larger the circle the higher the price. Even if the selling price is important, here it is the margin and the popularity that take precedence.
Finally, Omnes' laws bring together other techniques that complement this article, such as the customerprice response index to your price proposal for a range of dishes. How the price of restaurant dishes affects sales.